User Settings
User Settings are user configuration variables that can be re-used in your step configurations. Simply define the setting, and then make use of them within any of your steps.
It means you can change a parameter in all of the steps that use the setting in one go without needing to edit them all each time.
You can view any settings you have created by clicking onto the Settings tab.
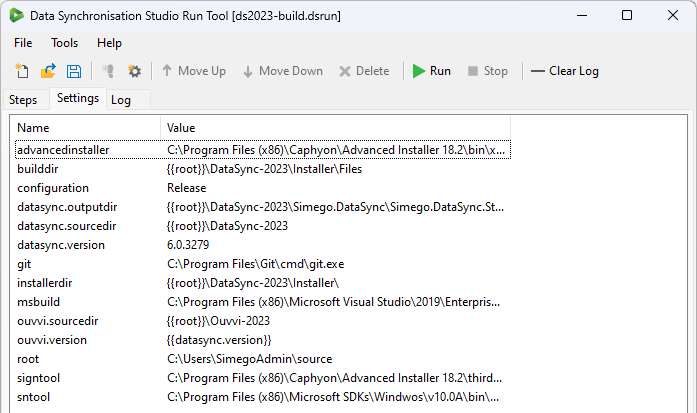
Create a Setting
To create a new user setting first click onto the Settings tab and then either use the shortcut button in the toolbar or open the file menu and select Add Setting.
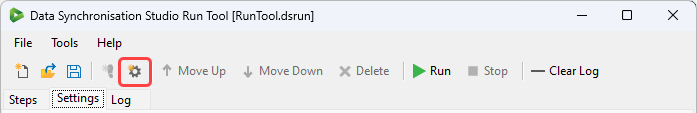
You then need to set a name and a value for your setting in the configuration window.
You can choose between three different types of user setting: User, User Encrypted, User Connection String.
- A User setting will show the value within the settings table.
- A UserEncrypted setting will encrypt the value.
- A UserConnectionString setting will encrypt the value at rest.
Using Settings
To use your settings in your step configurations you need to type the name inside two curly braces. For example {{MySetting}}.
An example of how you can use user settings is shown in the below screen capture using the external program step. User settings are being used to set the program, program arguments and working directory.
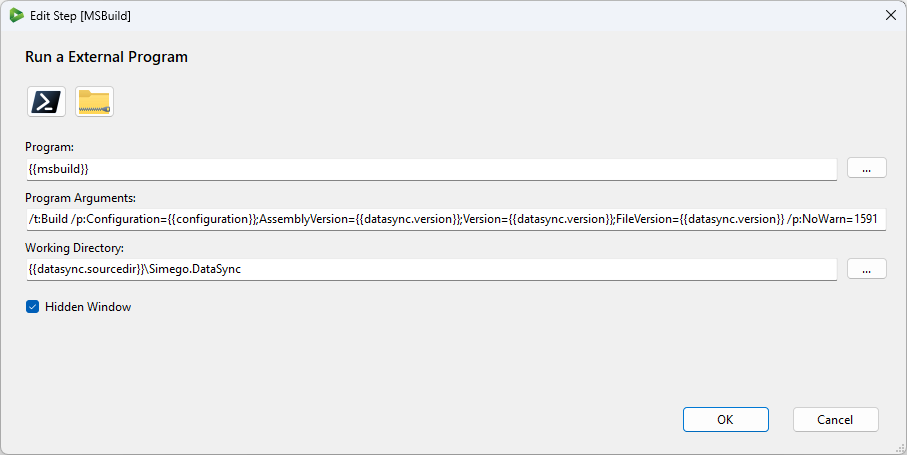
User Settings can also use other User Settings. Just enter them into the setting as you would if you were using the setting in your step configuration.
These settings within the settings tab would look similar to the below image.

To use User Settings within Data Sync projects you need to follow a similar process as is done fro Ouvvi User Settings.
Using User Settings in Data Sync Steps
To use a user setting inside a Data Sync step you need to start by adding the setting to the properties list.
This can be set in Data Sync by open the File menu and selecting Properties to open the property window. Then find the Properties field and click onto the ellipsis to open the collection manager window.
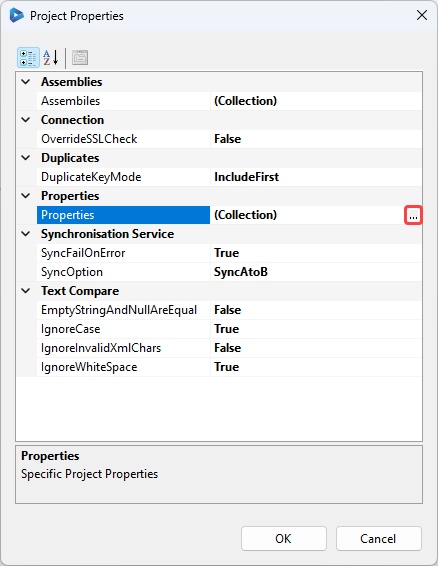
You can now add the setting to the list by entering the name from the RunTool. If you leave the value blank the value will be passed to Data Sync at run time by the Run Tool
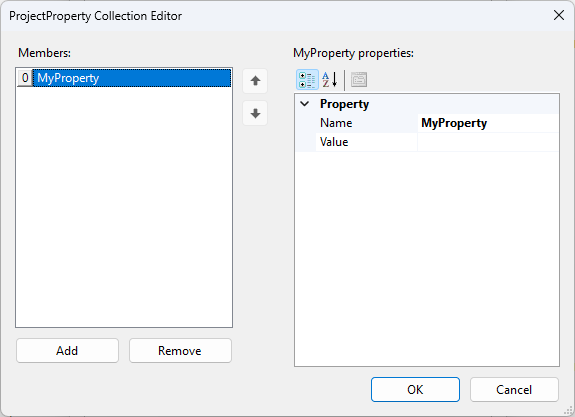
To use this property you need to use project automation to apply the value at runtime by adding code to the Start method. For example you could use the property modify the Where clause on the SQL provider.
To get a value you can access it by the indexer within Project Automation, i.e. Properties["MyVariable"]. You can see an example of setting a variable and then writing this to the output window in the image below:
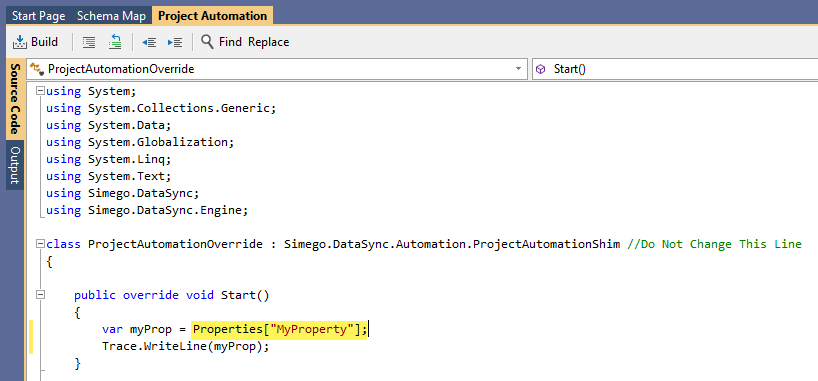
Now when a variable is updated in the Run Tool it will feed into the Data Sync step within that Run Tool project. This is the same process you would follow for Ouvvi User Settings.
Pass Settings at RunTime
You can dynamically pass settings into your project at Run Time, using either the built in settings or by using the Import Command Line Parameter step.
Pre-Configured Internal Settings
The Run Tool has a few built in settings, that are calculated at the point the Run Tool project is started.
Below is a table of all of the built in settings that you can make use of in your steps.
| Name | Setting | Example |
|---|---|---|
| DAY | {{DAY}} | 14 |
| MONTH | {{MONTH}} | 05 |
| YEAR | {{YEAR}} | 2021 |
| FILEDATE | {{FILEDATE}} | 2021-05-14 |
| DATE | {{DATE}} | 2021-05-14 |
| FILETIME | {{FILETIME}} | 134339 |
| TIME | {{TIME}} | 13:43:39 |
| HOUR | {{HOUR}} | 13 |
| MIN | {{MIN}} | 43 |
| SEC | {{SEC}} | 39 |
| MACHINE | {{MACHINE}} | MachineName |
| USERNAME | {{USERNAME}} | User1 |
| DOMAIN | {{DOMAIN}} | MyDomain |
| APPPATH | {{APPPATH}} | C:\Program Files\Simego\Data Synchronisation Studio 6.0 |
| PERSONAL | {{PERSONAL}} | C:\Users\User1\Documents |
| LOCALAPPLICATIONDATA | {{LOCALAPPLICATIONDATA}} | C:\Users\User1\AppData\Local |
| APPLICATIONDATA | {{APPLICATIONDATA}} | C:\Users\User1\AppData\Roaming |
| COMMONAPPLICATIONDATA | {{COMMONAPPLICATIONDATA}} | C:\ProgramData |
| PROGRAMFILES | {{PROGRAMFILES}} | C:\Program Files |
| PROGRAMFILESX86 | {{PROGRAMFILESX86}} | C:\Program Files (x86) |
| SYSTEM | {{SYSTEM}} | C:\WINDOWS\system32 |
| SYSTEMX86 | {{SYSTEMX86}} | C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64 |
| WINDOWS | {{WINDOWS}} | C:\WINDOWS\system32 |
| TEMP | {{TEMP}} | C:\Users\User1\AppData\Local\Temp\ |
| NEWGUID | {{NEWGUID}} | {87747ce2-ada0-4ae7-b603-240832ff37cf} |
| SMTPUsername | {{SMTPUsername}} | myemail@domain.com |
| SolutionName | {{SolutionName}} | RunToolProject |
| SolutionPath | {{SolutionPath}} | C:\Users\User1\source\repos\myRepo\RunToolProject |
| SolutionDataPath | {{SolutionDataPath}} | C:\Users\User1\source\repos\myRepo\RunToolProject.ds |