ODBC Database
The ODBC Database provider connects to a database using ODBC.
The following Databases are typically what you might connect with Data Sync via ODBC.
- Oracle
- SQL Server
- AS/400
- IBM DB2
- MySQL
- Postgres
- Teradata
- Netezza
- Amazon Redshift
- Amazon Aurora
Running 64-Bit Data Sync requires 64 Bit ODBC Drivers and configuration via 64 Bit ODBC Manager.
SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE SQL Statements are automatically calculated from the Data Schema. Only those columns in the Schema Map are affected the Key(s) columns define the WHERE condition for UPDATE and DELETE.
In Incremental Mode the IN clause is used to return matching records based on the Key selection in groups of 500 across multiple CPU threads. It is advised that the Key column is an Indexed SQL Column.
Connect
To connect to your Database using ODBC, in the connection window expand the SQL Database folder and select ODBC Database.
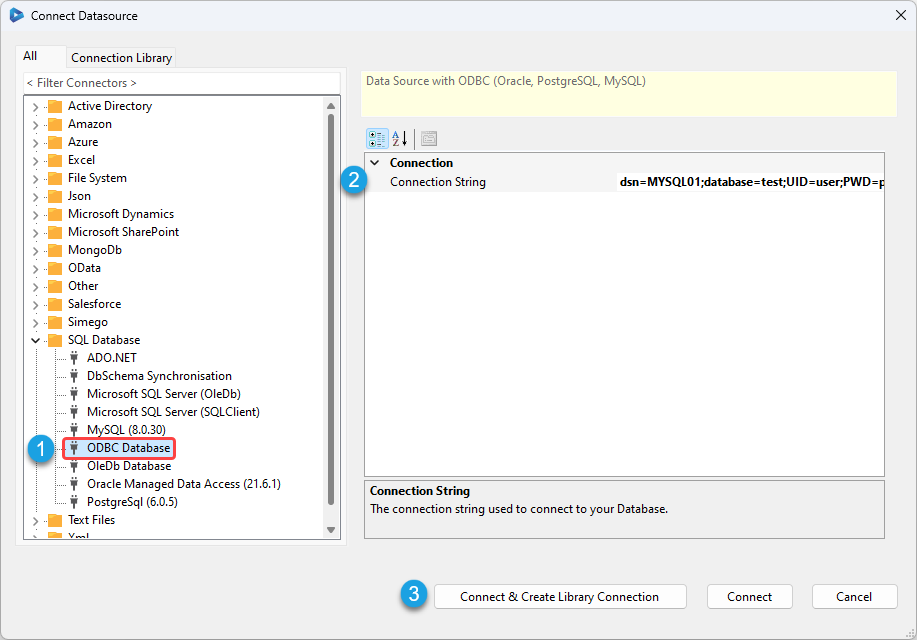
Enter in the connection string to connect to your database, you may need to include credentials to be able to access the data within the tables. Then click Connect & Create Library Connection to save the connection to the Database.
Enter in a name for the connection. This will load into the Connection Library window and you can access all of the objects found within that database. This means you only need to configure and save the connection once as you can re-use it in future projects as needed.
Connection Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| CommandTimeout | The number of seconds a command will run before a Timeout exception is thrown. |
| ConnectionString | The connection string used to connect to the ODBC Database. An example ODBC connection string when using connections created in ODBC Connection manager is: dsn=MYSQL01;database=test;UID=user;PWD=password |
| SourceTable | The Datasource Table or View name that the datasource is connected to. |
| Command | A user defined SQL Query to use instead of SourceTable. Setting this property overrides SourceTable and makes the Data source read-only. |
| CommandWhere | Appends an WHERE clause to the Query, only when using SourceTable if you have a user defined Query in Command this value is ignored. |
| CommandOrderBy | Appends an ORDER BY clause to the Query. |
| StartQuoteChar | A character used as the start character to escape identifiers. |
| EndQuoteChar | A character used as the end character to escape identifiers. |
| ParameterMarker | The character to use in parametrised queries, such as INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE statements. I.e. for MySQL its ? and for Postgres its :0 |
Project Automation
The SQL Server provider also exposes helper functions that can be called from Project Automation to update the Data source ExecuteScalar, ExecuteNonQuery and UpdateSourceRow.
ExecuteScalar
Method ExecuteScalar creates a SQL Command from the supplied SQL and Parameters values and calls ExecuteScalar against the database.
int ExecuteScalar(string sql, params object[] parameters)
ExecuteNonQuery
Method ExecuteNonQuery creates a SQL Command from the supplied SQL and Parameters values and calls ExecuteNonQuery against the database.
int ExecuteNonQuery(string sql, params object[] parameters)
UpdateSourceRow
Method UpdateSourceRow creates a SQL Command to update a single column in the Data source using the key from the DataCompareItem
bool UpdateSourceRow(string column, object value, DataCompareItemInvariant item)
Used to update the source row from project automation, for example setting a Sync flag once a record has been synchronised.
For example calling this method in the AfterUpdateItem item event to mark a record in the source as synchronised.
public override void AfterUpdateItem(object sender, DataCompareItemInvariant item, object identity)
{
DataSourceA.UpdateSourceRow("Sync", true, item);
}