Connecting to SQL Server (OleDB) in Data Sync
The Microsoft SQL Server (OleDB) is based on the System.Data.OleDB client library connect to a Microsoft SQL Server and Azure SQL Database instance.
SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE SQL Statements are automatically calculated from the Data Schema. Only those columns in the Schema Map are affected the Key(s) columns define the WHERE condition for UPDATE and DELETE.
In Incremental Mode the IN clause is used to return matching records based on the Key selection in groups of 500 across multiple CPU threads. It is advised that the Key column is an Indexed SQL Column.
Connect
To connect to your SQL Database using OleDB, in the connection window expand the SQL Database folder and select Microsoft SQL Server (OleDb).
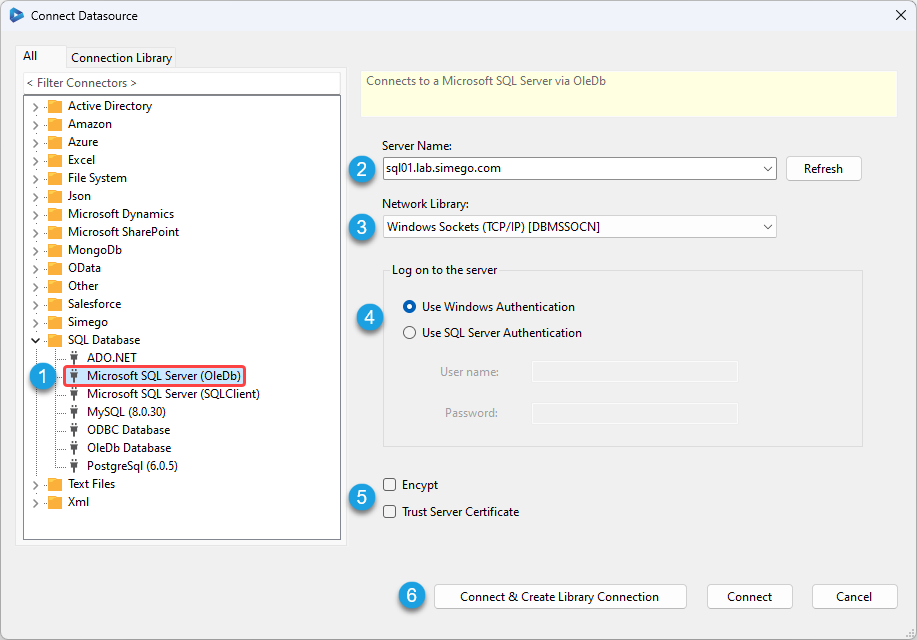
Enter in the server name, select a network library, any required credentials and determine if the connection should be encrypted and the Server Certificate trusted. Then click Connect & Create Library Connection to save the connection to the Database you select in the next window.
We have a few details below about the Server Name, Network Library and Authentication to help you connect to your SQl Server.
Server Name
Enter in the network name of your SQL Server, this can also be a SQL Instance e.g. SQL01\SQLEXPRESS .
Network Library
Make sure to select the Network Library used to connect to your SQL Server typically this is either TCP/IP or Named Pipes.
Authentication
You then need to enter the credentials to enable the connection to the SQL Server. You can choose between the current process (user) or a SQL Account.
Data source
After connecting a window will open where you need to select the database to connect to within your SQL Server, and a SQL object to connect to (table or view). Data Sync will provide a Tree View of your SQL Server Databases, Tables and Views, expand this to find the object to connect to.
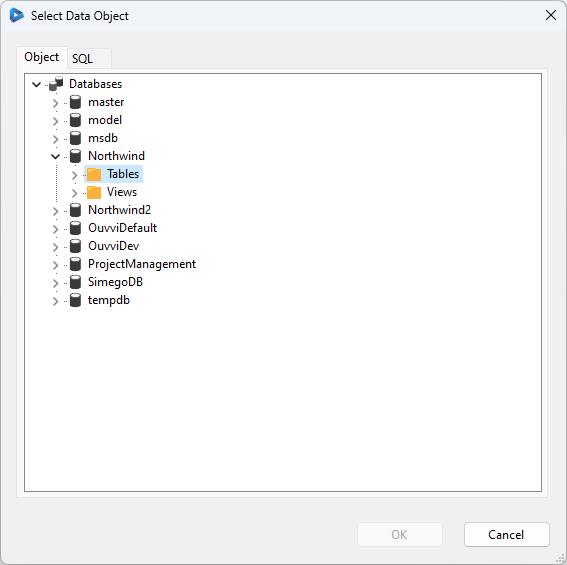
You can optionally enter a SQL Query via the SQL tab to select the data you want to work with. Specifying a SQL Query will make the data source read-only since Data Sync cannot work out how to update the data source from a user defined query.
If you previously clicked Connect & Create Library Connection then a window will appear where you can enter a name for the connection. This will load into the Connection Library window and you can access all of the SQL objects found within that database. This means you only need to configure and save the connection once as you can re-use it in future projects as needed.
Properties
CommandTimeout
The SQL Command timeout in seconds.
ConnectionString
The SQL Connection String that connects to your database.
SourceTable
The TABLE or VIEW that the Data source is connected to.
Command
A user defined SQL Query to use instead of SourceTable setting this property overrides SourceTable and makes the Data source read-only.
Data Sync wraps your command text so it appears as an inner query SELECT * FROM (<SQL_QUERY>) T1 to support schema discovery and CommandOrderBy property.
Stored Procedures
To call a Stored Procedure use the EXEC keyword i.e. EXEC spGetAllUsers. The EXEC keyword tells Data Sync to treat this query as a Stored Procedure.
CommandOrderBy
Appends an ORDER BY clause to the Query.
CommandWhere
Appends an WHERE clause to the Query, only when using SourceTable if you have a user defined Query in Command this value is ignored.
CommandBatchSize
Specifies the number of commands to send to SQL Server in one SQL statement. SQL Server supports a maximum number of parameters of 2000 so this value must be less than COLUMNS*BATCH.
Transaction
Specifies the number of commands per SQL Transaction.
Transaction > 0 will create a new Transaction on the connection.
BlobColumn
Defines a column that is a Binary data column where Data Sync uses a separate channel to SELECT and UPDATE this value. This prevents loading these large blob values on the read operation.
This is used with providers that support File based synchronisation operations such as
- FileSystem
- SharePoint Document Library
- Azure Blob Storage
- Amazon S3 Storage
- SQL Server
BlobName
Defines a column that returns the name of the Blob i.e. FileName when used with SharePoint.
Project Automation
The SQL Server provider also exposes helper functions that can be called from Project Automation to update the Data source ExecuteScalar, ExecuteNonQuery and UpdateSourceRow.
Using these methods on the Target connection with a Transaction > 0 will cause a DeadLock since a SQL Transaction is in place.
ExecuteScalar
Method ExecuteScalar creates a SQL Command from the supplied SQL and Parameters values and calls ExecuteScalar against the database.
int ExecuteScalar(string sql, params object[] parameters)
ExecuteNonQuery
Method ExecuteNonQuery creates a SQL Command from the supplied SQL and Parameters values and calls ExecuteNonQuery against the database.
int ExecuteNonQuery(string sql, params object[] parameters)
UpdateSourceRow
Method UpdateSourceRow creates a SQL Command to update a single column in the Data source using the key from the DataCompareItem
bool UpdateSourceRow(string column, object value, DataCompareItemInvariant item)
Used to update the source row from project automation, for example setting a Sync flag once a record has been synchronised.
For example calling this method in the AfterUpdateItem item event to mark a record in the source as synchronised.
public override void AfterUpdateItem(object sender, DataCompareItemInvariant item, object identity)
{
DataSourceA.UpdateSourceRow("Sync", true, item);
}
Troubleshooting
If you get the error The certificate chain was issued by an authority that is not trusted when you are trying to connect, then you need to ensure that you select the Trusted checkbox in the connection window.